Motor
Overview¶
The component MOTOR is a stepper driver for DRV8824/25 and A4988 breakout boards
Example
An example project for the Arduino IDE is provided in BasicStepperDriver.ino (download here)
| ESP Board | motor |
|---|---|
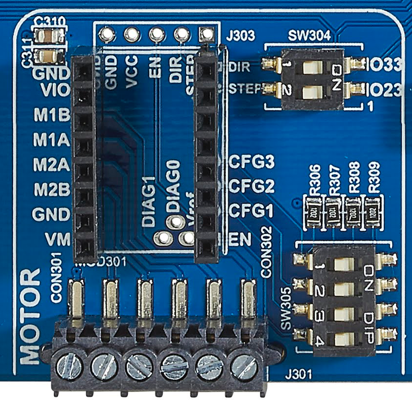 |
SW304,SW305 |
Activating the component¶
The component has two dip switches SW304 and SW305 for activating the component.
| Function | SWITCH | IO port | Conflicts with | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIR | SW304-1 | 33 | RGB LED, SW313, DIN; TFT, SW314, T_DO; mikroBus, SW405-6, AN | |
| STEP | SW304-2 | 23 | RFID, SW303-4, MOSI; TFT, SW311-4, MOSI; TFT, SW314-4, T_DIN; mikroBus, SW405-1, MOSI |
The four switchs of SW305 are connected to GND. The functions are as follows:
| Function | SWITCH |
|---|---|
| CFG3 | SW305-1 |
| CFG2 | SW305-2 |
| CFG1 | SW305-3 |
| EN | SW305-4 |
Connect a stepper motor on J301.
Motor connection from left to right:
| Function | SWITCH |
|---|---|
| GND | external motor power supply |
| VCC | external motor power supply |
| 2B | motor coil 2 |
| 2A | motor coil 2 |
| 1A | motor coil 1 |
| 1B | motor coil 1 |
Using the component¶
You have to switch on SW304. Depending on your motor driver, you may need to turn on Enable (switch 4 of SW305).
Setup the component¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | #include <Arduino.h> #include <BasicStepperDriver.h> // Motor steps per revolution. Most steppers are 200 steps or 1.8 degrees/step #define MOTOR_STEPS 200 // All the wires needed for full functionality #define DIR 33 #define STEP 23 // Since microstepping is set externally, make sure this matches the selected mode // 1=full step, 2=half step etc. #define MICROSTEPS 16 // 2-wire basic config, microstepping is hardwired on the driver BasicStepperDriver stepper(MOTOR_STEPS, DIR, STEP); |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | void setup() { /* * Set target motor RPM. * These motors can do up to about 200rpm. * Too high will result in a high pitched whine and the motor does not move. */ stepper.setRPM(100); } |
Control the servo¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | void loop() { // energize coils - the motor will hold position // stepper.enable(); /* * Tell the driver the microstep level we selected. * If mismatched, the motor will move at a different RPM than chosen. */ stepper.setMicrostep(MICROSTEPS); /* * Moving motor one full revolution using the degree notation */ stepper.rotate(360); delay(1000); /* * Moving motor to original position using steps */ stepper.move(-200*MICROSTEPS); // pause and allow the motor to be moved by hand // stepper.disable(); delay(1000); } |
Sample project¶
A sample project for the Arduino IDE is provided in BasicStepperDriver.ino (download here).